Padding
The padding clears an area around the content (inside the border) of an element. The padding is affected by the background color of the element.The top, right, bottom, and left padding can be changed independently using separate properties. A shorthand padding property can also be used, to change all paddings at once.
Possible Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| length | Defines a fixed padding (in pixels, pt, em, etc.) |
| % | Defines a padding in % of the containing element |
Padding - Individual sides
In CSS, it is possible to specify different padding for different sides:Example
padding-top:25px;
padding-bottom:25px;
padding-right:50px;
padding-left:50px;
padding-bottom:25px;
padding-right:50px;
padding-left:50px;
Padding - Shorthand property
To shorten the code, it is possible to specify all the padding properties in one property. This is called a shorthand property.The shorthand property for all the padding properties is "padding":
Example
padding:25px 50px;
- padding:25px 50px 75px 100px;
- top padding is 25px
- right padding is 50px
- bottom padding is 75px
- left padding is 100px
- padding:25px 50px 75px;
- top padding is 25px
- right and left paddings are 50px
- bottom padding is 75px
- padding:25px 50px;
- top and bottom paddings are 25px
- right and left paddings are 50px
- padding:25px;
- all four paddings are 25px




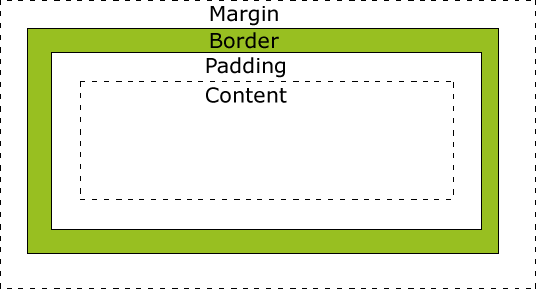 Explanation of the different parts:
Explanation of the different parts: Important: When you set the width and height properties of an
element with CSS, you just set the width and height of the content area. To
calculate the full size
of an element, you must also add the padding, borders and margins.
Important: When you set the width and height properties of an
element with CSS, you just set the width and height of the content area. To
calculate the full size
of an element, you must also add the padding, borders and margins.